
VMware vSphere Replication is a virtual machine data protection and disaster recovery solution. It is fully integrated with VMware vCenter Server and VMware vSphere Web Client, providing host-based, asynchronous replication of virtual machines. vSphere Replication is a proprietary replication engine developed by VMware that is included with VMware vSphere Essentials Plus Kit and higher editions of VMware vSphere, VMware vSphere with Operations Management editions, and VMware vCloud Suite editions.
vSphere Replication features and benefits
- Simple virtual appliance deployment minimizes cost and complexity.
- Integration with vSphere Web Client eases administration and monitoring.
- Protect nearly any virtual machine regardless of operating system (OS) and applications.
- Only changes are replicated, which improves efficiency and reduces network utilization.
- Recovery point objectives (RPOs) range from 15 minutes to 24 hours and can be configured on a
- per–virtual machine basis..
- Compatibility is provided with VMware Virtual SAN, traditional SAN, NAS, and local storage.
- Quick recovery for individual virtual machines minimizes downtime and resource requirements.
- Optional network isolation and compression help secure replicated data and further reduce network
- bandwidth consumption.
- Support for Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) and Linux file system quiescing improves reliability of recovered virtual machines
Architecture Overview
vSphere Replication 6.0 requires vCenter Server 6.0, either the Windows implementation or the Linux-based VMware vCenter Server Appliance. VMware vCenter Single Sign-On is also required. If using vSphere Replication with vCenter Site Recovery Manager, the versions of the two must be the same. For example, vSphere Replication 6.0 is the only version of vSphere Replication supported with vCenter Site Recovery Manager 6.0.
vSphere Replication is deployed as one or more prebuilt, Linux-based virtual appliances. A maximum of
10 vSphere Replication appliances can be deployed per vCenter Server. Each appliance is deployed with 4GB of memory and either two virtual CPUs—for small environments—or four virtual CPUs. A vSphere Replication virtual appliance is configured with two virtual machine disk (VMDK) files totaling 18GB in size.
Because vSphere Replication is host-based replication, it is independent of the underlying storage and it works with a variety of storage types including Virtual SAN, traditional SAN, NAS, and direct-attached storage (DAS). Unlike many array replication solutions, vSphere Replication enables virtual machine replication between heterogeneous storage types. For example, Virtual SAN to DAS, SAN to NAS, and SAN to Virtual SAN. vSphere Replication can, of course, replicate virtual machines between the same types of storage, such as Virtual SAN to Virtual SAN.
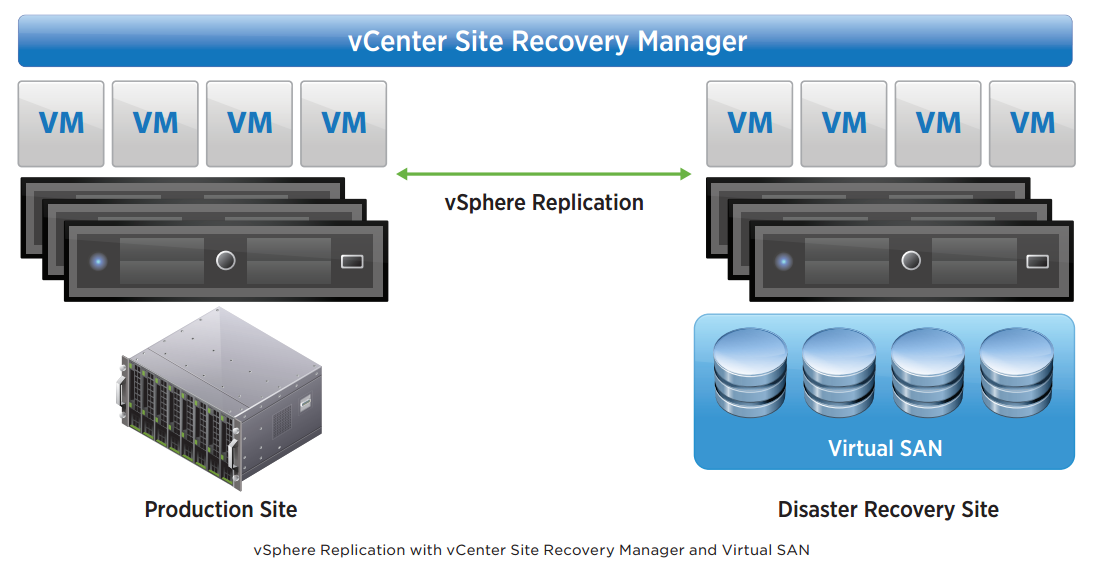
vSphere Replication can also serve as the replication engine for vCenter Site Recovery Manager. In this scenario, vSphere Replication virtual appliances are deployed at both the source and target locations, as with vCenter Site Recovery Manager. Replication is configured on a per–virtual machine basis, enabling fine control and selection of the virtual machines that are included in vCenter Server Site Recovery Manager protection groups and recovery plans. Use of vCenter Site Recovery Manager to protect virtual machines running on Virtual SAN requires vSphere Replication.
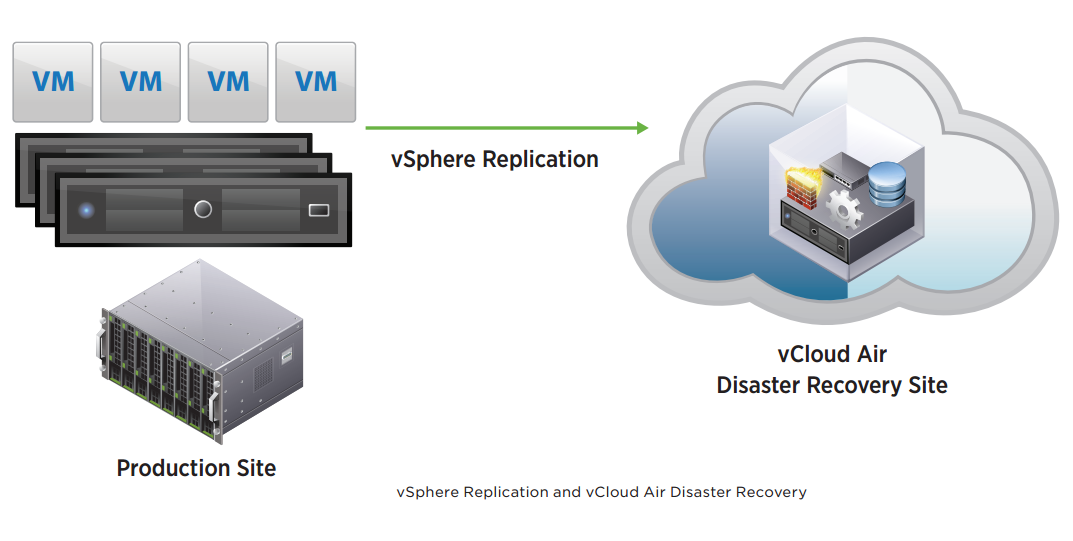
vCloud Air Disaster Recovery utilizes vSphere Replication to replicate virtual machines from an on-premises location to a vCloud Air data center. A subscription to vCloud Air Disaster Recovery is required and enables the failover of virtual machines to a vCloud Air data center in the event of a disaster. vCloud Air Disaster Recovery also enables test failover without impact to production workloads. Migration of workloads from vCloud Air back to an on-premises location following a disaster recovery is also supported.
Initial Deployment and Configuration
A vSphere Replication virtual appliance is deployed from an Open Virtualization Format (OVF) file using
vSphere Web Client. After the appliance has been deployed and powered on, a Web browser is used to
access the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) to finalize configuration.
The components that transmit replicated data are built into vSphere. There is no need to install or configure
these components, further simplifying vSphere Replication deployment. The first virtual appliance deployed
is referred to as the vSphere Replication management server. It contains the necessary components to receive replicated data, manage authentication, maintain mappings between the source virtual machines and the replicas at the target location, and provide support for vCloud Air Disaster Recovery and vCenter Site Recovery Manager. In many cases, this is the only appliance that must be deployed to enable vSphere Replication protection.
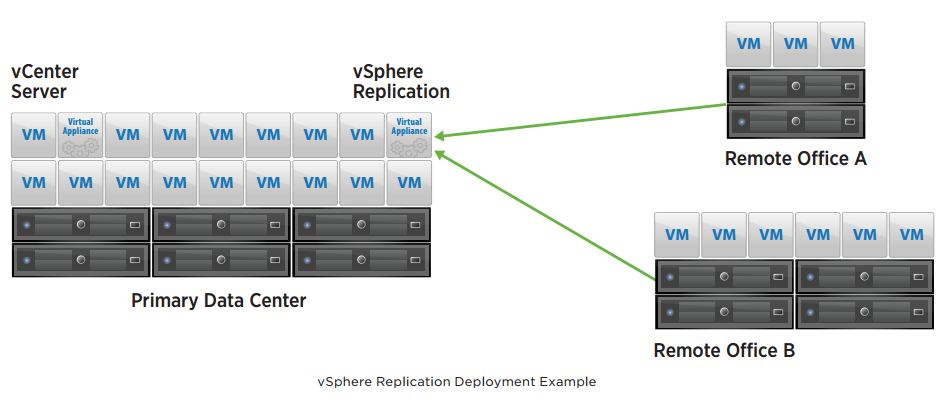
Additional vSphere Replication appliances can be deployed to support larger-scale deployments and topologies with multiple target locations. These additional virtual appliances are referred to as vSphere Replication servers.They do not contain the management components found in the vSphere Replication management server and are used only to receive replicated data. In addition to the vSphere Replication management server, as many as nine vSphere Replication servers can be deployed to a vCenter Server environment, for a maximum of 0 deployed vSphere Replication virtual appliances.
Network traffic isolation for vSphere Replication can be configured to improve performance and security. Configuration consists of dedicating a network connection to vSphere Replication on the source and destination hosts as well as adding one or more virtual network interface cards to each vSphere Replication virtual appliance to segregate replication traffic and management traffic. vSphere Network I/O Control can be used to control vSphere Replication bandwidth utilization.
Replication Process
vSphere Web Client configures replication for a virtual machine. Replication for one or more virtual machines can be selected and configured via the same workflow. When configuring replication, an administrator specifies items such as the virtual machine storage policy, RPO, VSS or Linux file system quiescing, and network compression of replication traffic. Virtual machine snapshots are not used as part of the replication process unless VSS quiescing is enabled.
The target location for vSphere Replication can be within the same vCenter Server environment, in another vCenter Server environment with vSphere Replication deployed, or a vCloud Air Disaster Recovery virtual data center.
The following articles will take you through the steps to deploy and configure vSphere Replication Appliance including the recovery procedure of virtual machines in case of disaster.
- Preparing vCenter Server for vSphere Replication 6
- Deploying vSphere Replication Appliance
- Configuring vSphere Replication 6
The introduction and vSphere replication explanation contents was taken directly from VMware